Enchroma Lenses for Colorblindness

How Do EnChroma Glasses Work?
Color blindness, a long-standing challenge for many, meets its match with Enchroma lenses. These cutting-edge glasses act as color filters, skillfully separating specific wavelengths of light to address any abnormalities in the red and green receptors, the culprits behind color confusion.
By fine-tuning the light spectrum, Enchroma’s lenses enable your brain to perceive colors more accurately, unraveling a vibrant tapestry of hues previously concealed
Is Color Blindness Common?
Approximately 1 in 12 men and 1 in 200 women experience some degree of color blindness. The most common type is “red-green color blindness,” scientifically known as color vision deficiency. It occurs when retinal cone cells respond differently to light than usual. While people with color blindness can still see colors, they often struggle with distinguishing certain pairs of colors.
Different Types of Colorblindness
Is Color Blindness Common?
Let us help you Ignite your senses with Enchroma Lenses. Rediscover the richness of colors you’ve been missing.
Schedule an appointment with Cockrell Eyecare Center.
According to genetic population statistics it is estimated that 4 out of 5 cases are forms of partial color blindness (also called anomalous trichromacy) which are addressable using the EnChroma optical lens technology.
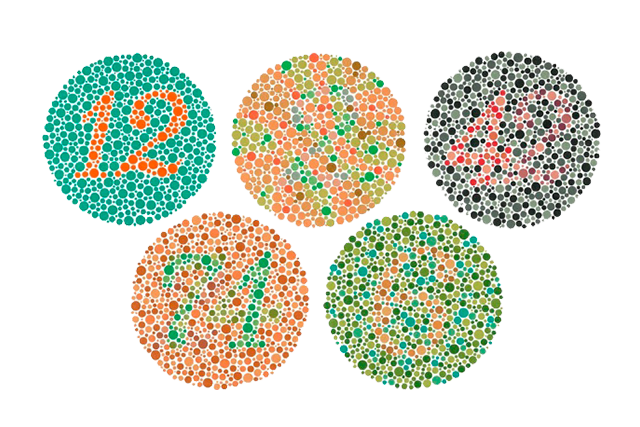

Are You Color Blind?
Try the EnChroma Color Vision Test
Color Blindness - Color Vision Deficiency
Approximately 1 in 12 men and 1 in 200 women have some degree of color blindness. There are different types of color blindness but the most common is known as ‘red-green color blindness.’
Color blindness (also called color vision deficiency by vision scientists), is a condition in which the retinal cone cells respond to light differently than normal. People with color blindness can usually still see colors but have color confusions or see certain pairs of colors so similarly that they cannot tell them apart.
Check out some designer frames we carry at our Cockrell Eyecare Center optical.
TYPES OF COLOR BLINDNESS

Deutan Color Blindness
Deutan color blindness (also known as deuteranomaly) is a type of red-green color blindness in which the green cones in the eye detect too much red light and not enough green light.
As a result red, yellow, green, and brown can appear similar, especially in low light. It may also be difficult to tell the difference between blues and purples, or pinks and grays. Learn more about Deutan and other types ofcolor blindness.
Protan Color Blindness
Protans are people with protanomaly, a type of red-green color blindness in which the red cones do not detect enough red and are too sensitive to greens, yellows, and oranges.
As a result, greens, yellows, oranges, reds, and browns may appear similar, especially in low light. It can also be difficult to tell the difference between blues and purples, or pinks and grays. Red and black might be hard to tell apart, especially when red text is against a black background. Learn more about Protan and other types of color blindness.


Tritan Color Blindness
Tritan-type color vision is characterized by a loss of color discrimination for shades of blue and yellow but it is not typically a form of color blindness.
This can be caused by age-related factors, genetic factors, as well as exposure to certain toxins such as mercury. A complete diagnosis of color vision deficiency is not possible using online testing–consult an eye care professional for more information.
